Cupping and Gua sha
Cupping and Gua sha have been used for centuries in East Asia to remove stagnation in the body. Both use different techniques to move blood, improve circulation and relieve pain.
Both techniques can be used alone or alongside acupuncture needles. They help relieve the symptoms of chronic and acute pain and stiff, tight muscles and can also aid the immune system to encourage the release of symptoms such as coughs, colds and breathing difficulties.
What is cupping?

Cupping is a widely-used technique that involves applying a vacuum to the skin in the form of a glass or plastic cup and air is removed. The cup is either left in place for several minutes or moved around the affected body part providing a pleasant massage-like sensation.
The cup draws blood to the area, nourishes the muscles, removes stagnation from the area and helps to relieve pain.
Cupping does leave a bruise-like mark on the skin, but this will usually disappear within 2-3 days.
Benefits of cupping
- Encourages overall circulation
- Alleviates adhesions by lifting, separating and hydrating the muscle tissues
- Clears inflammation, congestion and stagnation of the skin, muscles, bones, joints and organs
- Reduces pain by releasing tension
- Rebuilds healthy tissue and helps the body to regenerate
What is Gua sha?
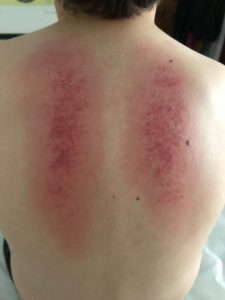
Like cupping, Gua sha is a healing technique that draws blood to the area, nourishes the muscles and removes stagnation. Instead of a cup, a ‘press-stroking’ technique using an instrument is applied to a lubricated area of the body.
Gua sha can relieve symptoms including:
- Neck and shoulder pain
- Back pain
- Headaches and migraine
- Jaw clenching
- Frozen shoulder
- Tennis or golfers elbow
- Soft tissue injury
- Spondylosis
- Scoliosis
- Upper respiratory infections or difficulty breathing
Gua sha leaves a red, bruise-like mark on the surface of the skin which disappears after 2-3 days. The marks are not painful. These marks are a good indicator of what is happening in the body and where the stagnation is situated.
Patients request Gua sha to relive tight muscles alongside their acupuncture treatment.